Solar System: Definition, Location, Formation, Length, Objects
A solar system is a collection of celestial bodies orbiting a central star. Our solar system contains eight planets, five dwarf planets, over 190 known moons, and numerous smaller objects. The Sun contains 99.8% of the solar system’s total mass. Solar system objects include planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and Kuiper belt objects.
Our solar system is located in the Milky Way galaxy’s Orion Arm, a minor spiral arm. The solar system resides 27,000 light-years from the galactic center on the inner rim. The Orion Arm is situated between the Sagittarius Arm and the Perseus Arm. The solar system is positioned approximately 25,000 light-years from the galactic center.
The solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago from a massive gas and dust cloud called the solar nebula. A nearby supernova explosion triggered the nebula’s collapse. The collapsing cloud spun faster and flattened into a disk. The sun formed at the center through accretion. Surrounding disk cooled, and particles combined to form planets through accretion.
The solar system’s length measures approximately 2 light-years. The Oort Cloud’s outer boundary marks this extent. The distance equals 18.84 trillion kilometers or 11.7 trillion miles from the Sun. The solar system’s diameter ranges between 36-39 billion kilometers when excluding the Oort Cloud. Neptune’s orbit marks the boundary of the solar system when the Oort Cloud is not considered.
Objects in our solar system include the Sun, eight planets, five dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteoroids, and interplanetary dust. The solar system contains over 1 million asteroids larger than 1 km in diameter. An estimated 100 billion comets reside in the Oort Cloud. Human-made objects include artificial satellites and space stations, with over 8,000 orbiting Earth alone.
Solar System is the widely accepted name for our star system. The Sun, derived from Latin “solis,” forms the central object. Scientists sometimes refer to it as the Sol System. The Solar System contains planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets orbiting the Sun. The Solar System orbits the center of the Milky Way galaxy at a speed of 220 kilometers per second.
The solar system orbits the Milky Way galaxy in approximately 225-250 million years. Astronomers call this period a galactic year or cosmic year. The solar system completes one orbit around the galactic center at an average speed of 220 km/s. Harlow Shapley and Jan Oort contributed to determining this orbit duration in the early 20th century.
The sun star sits at the center of our solar system. Solar system objects revolve around the sun. The sun’s gravity holds everything together, including planets and asteroids. The sun provides energy, light, and heat for objects in space. The sun comprises 99.8% of the solar system’s mass and has 330,000 times Earth’s mass.
Solar systems consist of a central star and orbiting celestial bodies. Galaxies contain billions of stars, stellar remnants, gas, and dust. Solar systems have a single star, while galaxies house billions of stars. Solar systems are centered around one star, while galaxies are centered around a supermassive black hole. Solar systems exist as part of a larger galaxy, while galaxies form the building blocks of the universe.
The solar system is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Scientists estimate this age using radiometric dating of meteorites. The oldest known stars in our galaxy support this estimate. The solar system formed from a collapsing dust and gas cloud. The universe is estimated to be approximately 13.8 billion years old, meaning our solar system formed about 9.2 billion years after the Big Bang.
The inner solar system contains four planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The outer solar system comprises four planets furthest from the Sun: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Inner planets are rocky and smaller, with diameters ranging from 4,879 km to 12,742 km. Outer planets are gaseous and larger, with diameters spanning from 49,528 km to 142,984 km.
The edge of the solar system starts around 2,000 AU from the sun. The Oort Cloud extends from 2,000 to 100,000 astronomical units (AU) away from the sun. One AU equals 93 million miles or 149.6 million kilometers. Voyager 1, at 12.5 billion miles, would take 70,000 years to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud. Neptune, the outermost planet, orbits at an average distance of 4,000,000,000 kilometers from the Sun.
One million Earths could fit inside the Sun, demonstrating its immense size. The Sun accounts for 99% of the solar system’s mass. Jupiter’s largest moon, Ganymede, has a salty ocean with more water than Earth. Uranus spins sideways with its axis tilted at 98 degrees, causing extreme seasons. Venus is the hottest planet, with surface temperatures reaching 462°C (863°F). The solar system’s mass totals approximately 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms, with the Sun comprising the vast majority.
What is a solar system?
A solar system is a collection of celestial bodies orbiting a central star. Solar systems consist of a star, planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other smaller objects bound by gravity. Our solar system contains eight planets, five dwarf planets, over 190 known moons, and numerous smaller bodies.
Solar system facts reveal a gravitationally bound system dominated by a central star. The Sun contains about 99.8% of the solar system’s total mass. Solar system objects include planets, dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and Kuiper belt objects. Scientists estimate the solar system to be around 4.6 billion years old.
Solar system planets are divided into two main categories: terrestrial planets and gas giants. The four inner terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) have rocky compositions. The four outer gas giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune) have gaseous compositions. Neptune orbits at an average distance of 4.5 billion kilometers from the Sun.
Solar system terms include orbit, eccentricity, perihelion, and aphelion. Orbit describes the path an object follows as it revolves around the Sun or a planet. Eccentricity measures how elliptical an object’s orbit is. Perihelion refers to the point in an object’s orbit closest to the Sun.
Solar system labeled diagrams include the Sun, planets, asteroid belt, Kuiper Belt, and Oort Cloud. The solar system spans a diameter of about 287.46 billion kilometers. The heliosphere, a vast diffuse cloud of gas and dust, exists within the solar system.
What are the planets in order in our solar system?
The planets in order in our solar system are listed below.
- Mercury
- Venus
- Earth
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune
The planets in our solar system orbit the Sun in a specific order. Mercury occupies the first position, located at an average distance of 58 million kilometers from the Sun. Venus follows as the second planet, orbiting at 108 million kilometers from the Sun. Earth exists as the third planet, positioned 149.6 million kilometers from the Sun. Mars holds the fourth position, situated 227.9 million kilometers from the Sun. Jupiter stands as the fifth and largest planet, orbiting at 778.3 million kilometers from the Sun. Saturn occupies the sixth position, located 1.43 billion kilometers from the Sun. Uranus resides as the seventh planet, positioned 2.88 billion kilometers from the Sun. Neptune exists as the eighth and farthest known planet, orbiting at 4.49 billion kilometers from the Sun.
The planets are divided into two groups based on their composition. Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars comprise the inner planets with rocky compositions. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune form the outer planets with gaseous compositions. The planets increase in size from inner to outer positions, with Jupiter holding the title of largest planet. The planets increase in moon count from inner to outer positions, with Saturn possessing the most moons at 146.
How many planets are in the Earth’s solar system?
Earth’s solar system contains eight planets. Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune orbit the Sun. These celestial bodies meet the International Astronomical Union’s criteria for planet classification. Gas giants Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are larger. Rocky planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars are smaller. Pluto is classified as a dwarf planet.
Which planet is the largest in the solar system?
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. Jupiter’s diameter measures approximately 88,846 miles (142,984 kilometers), over 11 times Earth’s diameter. Jupiter’s mass exceeds Earth’s by 318 times. Jupiter comprises 2.5 times the combined mass of all other solar system planets. Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, orbits at an average distance of 483.8 million miles (778.3 million kilometers).
Jupiter’s mass dominates the solar system. The behemoth weighs in at 318 times Earth’s mass, totaling an astounding 1,898,187,000,000,000,000,000,000 kg. Jupiter’s mass surpasses the combined mass of all other planets. Mars, by comparison, has a diameter of only 6,794 km, less than 5% of Jupiter’s girth.
Jupiter’s immense size and mass result from its composition as a gas giant. The planet consists primarily of hydrogen and helium gases, giving it a lower density than Earth. Jupiter’s rapid rotation causes a noticeable bulge at its equator, contributing to its oblate spheroid shape.
Which planet is the smallest in our solar system?
Mercury is the smallest planet in our solar system. Mercury’s diameter measures 4,879 kilometers, less than half of Earth’s size. Mercury’s volume is 1/18th of Earth’s. Mercury is smaller than Earth’s moon, with 2/5 its diameter. Mercury’s mass equals 1/20th of Earth’s at 330,220,000,000,000 kilograms.
How many stars are there in our solar system?
Our solar system contains one star. The Sun is the only star in our solar system. Solar systems have one central star. Eight planets orbit the Sun in our solar system. Hundreds of thousands of other solar systems exist in the Milky Way galaxy, each with its own star.

Zero stars exist in our solar system if excluding the Sun. Some scientists debate the existence of a hypothetical brown dwarf companion called Nemesis. Two stars would exist in our solar system if Nemesis were confirmed. Observations have not yet detected Nemesis or any other star-like objects within our solar system’s boundaries.
Over 1,000,000 stars are visible to the naked eye on Earth. These visible stars exist in the Milky Way galaxy but are not part of our solar system. The Milky Way galaxy contains an estimated 200-400 billion stars. Stars exist in vast numbers throughout the observable universe, with trillions of stars across billions of galaxies.
Where is our solar system located in the universe?
The solar system is located in the Milky Way galaxy’s Orion Arm, a minor spiral arm. Milky Way contains two major arms and several minor arms. Solar system resides 27,000 light-years from the galactic center on the inner rim. Sun orbits with dozens of neighboring stars in a vast celestial structure.
The solar system resides in the Orion Arm, known as the Orion Spur. The Orion Arm is situated between the Sagittarius Arm and the Perseus Arm on an outer spiral arm of the galaxy. The solar system is positioned approximately 25,000 light-years from the galactic center. It occupies a location about two-thirds of the distance from the center to the edge of the galaxy. The solar system is roughly 25,000 light-years from the galactic rim.

The Milky Way galaxy belongs to the Local Group of galaxies. The Local Group includes other notable galaxies such as the Andromeda Galaxy and the Triangulum Galaxy. The solar system moves through the galaxy in a circular orbit around the galactic center. Billions of other solar systems exist in the Milky Way, many with similar characteristics and locations within the galaxy.
How was the solar system forming?
The solar system formed 4.6 billion years ago from a massive gas and dust cloud called the solar nebula. A nearby supernova explosion triggered the nebula’s collapse. The collapsing cloud spun faster, flattened into a disk. The sun formed at the center. Surrounding disk cooled, particles combined to form planets through accretion.
The Sun formed at the center of the solar nebula through accretion. Gas and dust collected and stuck together, igniting nuclear fusion reactions in the Sun’s core. The Sun’s formation released enormous energy, heating surrounding material and causing it to expand outward.

Planets took shape as material in the collapsing disk collided and merged. Rocky planets like Earth formed close to the Sun due to intense heat. Gas giant planets formed farther from the Sun where ices could exist. Smaller objects and materials built up the planets through accretion over millions of years.
The solar system’s formation involved key processes of collapse, contraction, and accretion. Gravity pulled material toward the center of the collapsing cloud, heating it to millions of degrees Kelvin. The solar nebula surrounded the forming Sun and flattened into a disk as it cooled. Dust and rock particles stuck together in the cooling nebula, forming larger bodies called planetesimals. Planetesimals collided and merged to form planets, which maintained their orbits due to conservation of angular momentum.
Which objects formed last in the solar system?
The objects that formed last in the solar system are listed below.
- Inner planets formed last in the solar system’s formation process.
- Earth, Mars, Venus, and Mercury took shape approximately 4.5 billion years ago.
- These inner planets formed about 100 million years after the initial solar system formation.
- Planetesimals formed first in the planetary formation sequence around 4.6 billion years ago.
- Inner planets formed next through the accretion of planetesimals.
- Protoplanets grew large enough to undergo differentiation, resulting in distinct crusts, mantles, and cores.
- Outer planets formed last, with Jupiter and Saturn completing their formation around 4.4 billion years ago.
- The final arrangement of our solar system reflects this formation sequence.
- Inner planets lie closest to the Sun, composed primarily of rock and metal.
- The asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter’s orbits, containing objects that never coalesced into a planet.
- Outer planets lie in the distant regions of the solar system, consisting mainly of hydrogen and helium gases.
- Gas giant moons formed as the very last objects in the solar system, around 4.3 billion years ago.
- These moons formed from disk material surrounding the newly formed planets.

Kuiper Belt Objects formed last in the solar system. Kuiper Belt Objects include dwarf planets like Pluto. KBOs formed 10-30 million years after the Sun’s formation. Inner planets formed much earlier, within 10-20 million years after the Sun’s birth. Rocky material condensed 4.5 billion years ago to form inner planets.
Planetesimals formed first in the planetary formation sequence. These small rocky bodies coalesced from the solar nebula around 4.6 billion years ago. Inner planets formed next through the accretion of planetesimals. Protoplanets grew large enough to undergo differentiation, resulting in distinct crusts, mantles, and cores. Outer planets formed last, with Jupiter and Saturn completing their formation around 4.4 billion years ago.
The final arrangement of our solar system reflects this formation sequence. Inner planets lie closest to the Sun, composed primarily of rock and metal. The asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter’s orbits, containing objects that never coalesced into a planet. Outer planets lie in the distant regions of the solar system, consisting mainly of hydrogen and helium gases. Gas giant moons formed as the very last objects in the solar system, around 4.3 billion years ago, from disk material surrounding the newly formed planets.
What is the length of solar system?
Solar system’s length measures approximately 2 light-years. Oort Cloud’s outer boundary marks this extent. Distance equals 18.84 trillion kilometers or 11.7 trillion miles from Sun. Astronomers estimate Oort Cloud extends 100,000 astronomical units outward. Light-speed traveler would reach outer boundary in about 2 years.
The solar system’s diameter ranges between 36-39 billion kilometers when excluding the Oort Cloud. This measurement corresponds to 240-260 AU in diameter. Neptune’s orbit marks the boundary of the solar system when the Oort Cloud is not considered.
Astronomers use the astronomical unit (AU) to measure distances within the solar system. One AU equals the average distance between Earth and the Sun, approximately 149.6 million kilometers. The solar system’s immense size demonstrates the vastness of space, with ongoing research and debate about its exact dimensions.
What objects are in our solar system?
The objects in our solar system are listed below.
- Sun
- Mercury
- Venus
- Earth
- Mars
- Jupiter
- Saturn
- Uranus
- Neptune
- Ceres
- Pluto
- Haumea
- Makemake
- Eris
- Moons (natural satellites)
- Asteroids
- Comets
- Meteoroids
- Interplanetary dust
- Helium focusing cone
- Gas and dust
- Solar wind
- Rings (around gas giant planets)
- Human-made objects (artificial satellites, space stations, etc.)
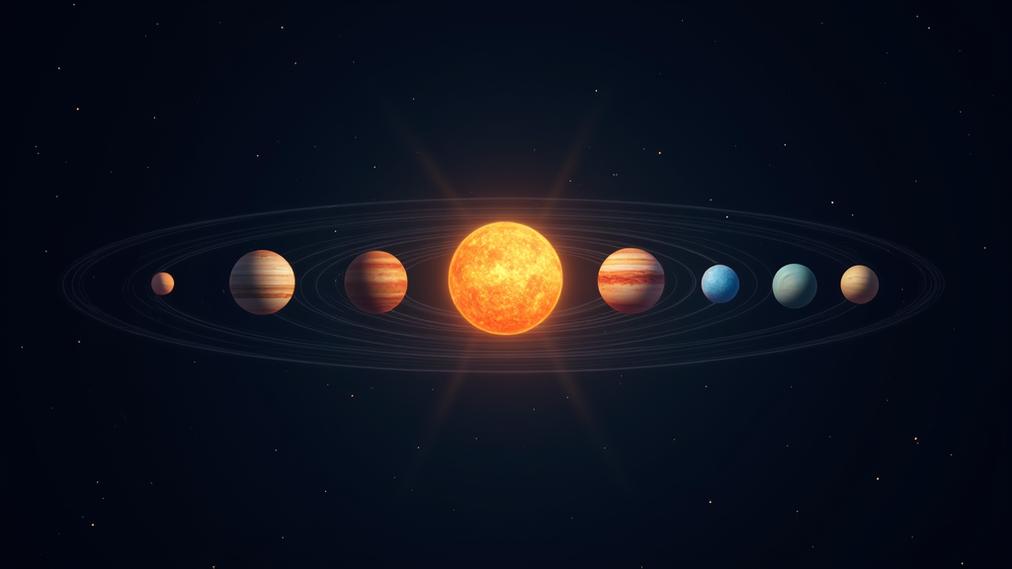

The solar system contains eight planets orbiting the sun. Five dwarf planets, including Pluto, exist within the system. Numerous moons accompany planets, with Saturn boasting 62 confirmed satellites. Millions of asteroids populate the asteroid belt. Comets originate from the outer solar system, releasing gas and dust when approaching the sun.
Moons are natural satellites orbiting planets and dwarf planets. Earth has one moon, while other planets have multiple moons. Jupiter hosts 79 known moons, Saturn has 62, Uranus possesses 27, and Neptune harbors 14. Asteroids populate our solar system, with over 1 million objects larger than 1 km in diameter. Comets are icy bodies that release gas and dust when approaching the Sun, with an estimated 100 billion comets residing in the Oort Cloud.
Meteoroids are small rocks or debris that enter planetary atmospheres. Meteors appear as shooting stars when meteoroids burn up completely in the atmosphere. Interplanetary dust fills the space between planets, produced by asteroid collisions, cometary activity, or planetary atmospheres. The helium focusing cone is a region around the Sun where solar magnetic fields concentrate helium ions.
Gas and dust exist throughout the solar system in various forms. Solar wind streams charged particles emitted by the Sun. Rings orbit the gas giant planets, with Saturn’s rings measuring 420,000 km in diameter. Human-made objects include artificial satellites, space stations, and other launched objects, with over 8,000 orbiting Earth alone.
What is the name of our solar system?
Solar System is the widely accepted name for our star system. Sun, derived from Latin “solis,” forms the central object. Solar System contains planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets orbiting the Sun. International Astronomical Union hasn’t officially named it. Scientists refer to it as Sol System. Milky Way galaxy houses our Solar System.
Alternative names are sometimes used informally. “Sol System” is occasionally employed, derived from the Latin word for sun. “Sun System” is another variation, directly referencing our central star. “Helios System” appears in some contexts, in science fiction, drawing from the Greek name for the sun god. “Terra System” is less common but occasionally used, referencing Earth (Terra in Latin).
The Solar System consists of eight planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and other celestial bodies. The Solar System has a star at its center, the Sun, which accounts for 99.8% of the system’s total mass of 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms. The Solar System includes over 190 known moons orbiting the planets and dwarf planets. Solar System objects orbit the Sun in elliptical paths due to its gravitational pull. The Solar System orbits the center of the Milky Way galaxy at a speed of 220 kilometers per second, located approximately 27,000 light-years from the galactic center.
How long does it take the solar system to orbit the Milky Way galaxy?
The solar system orbits the Milky Way galaxy in approximately 225-250 million years. Astronomers call this period a galactic year or cosmic year. The solar system completes one orbit around the galactic center at an average speed of 220 km/s. Harlow Shapley and Jan Oort contributed to determining this orbit duration in the early 20th century.
What is at the center of our solar system?
The sun star sits at the center of our solar system. Solar system objects revolve around the sun. Sun’s gravity holds everything together, including planets and asteroids. Sun provides energy, light, and heat for objects in space. Sun comprises 99.8% of the solar system’s mass and has 330,000 times Earth’s mass.

Which planet in our solar system is closest to the sun?
Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun in our solar system. Mercury orbits at an average distance of 58 million kilometers from the Sun. Mercury is the smallest planet, with a diameter of 4,879 kilometers. Mercury completes one orbit around the Sun in 88 Earth days. Mercury experiences extreme temperature variations from -173°C to 427°C.

Mercury’s small size and close proximity to the Sun result in extreme temperature fluctuations. Mercury has a diameter of 4,879 km, making it the smallest planet in the solar system. Mercury’s dayside temperature reaches over 430°C due to its proximity to the Sun. Mercury’s nighttime temperature drops to -180°C, lacking an atmosphere to retain heat. Mercury is one of five planets visible to the naked eye, known to ancient civilizations along with four other planets.
Which planet is closest to our solar system?
Mercury is the closest planet to our solar system. Mercury orbits closest to the Sun at an average distance of 58 million kilometers. Mercury is the smallest planet, with a diameter of 4,879 kilometers. Mercury’s closest approach to the Sun is 46 million kilometers, while its farthest point is 70 million kilometers away.
What is the difference between solar system and galaxy?
Solar systems consist of a central star and orbiting celestial bodies. Sun forms 99.8% of our solar system’s mass. Planets, moons, asteroids, and comets orbit the sun. Galaxies contain billions of stars, stellar remnants, gas, and dust. Milky Way galaxy includes our solar system. Galaxies span trillions of stars and celestial objects.
The composition of solar systems and galaxies varies greatly. Solar systems consist of one star, planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. Galaxies contain billions of stars, solar systems, nebulae, black holes, and dark matter. The number of stars in each structure is vastly different. Solar systems have a single star, like our Sun. Galaxies house billions of stars, with the Milky Way containing an estimated 200-400 billion stars.

Gravitational centers differ between solar systems and galaxies. Solar systems are centered around one star, which comprises about 99.8% of the system’s total mass. Galaxies are centered around a supermassive black hole, with stars, gas, and dust orbiting this central point. The location within the cosmic hierarchy distinguishes solar systems from galaxies. Solar systems exist as part of a larger galaxy. Galaxies form the building blocks of the universe, belonging to galaxy clusters and superclusters within the cosmic web.
What is the age of our solar system?
The solar system is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Scientists estimate this age using radiometric dating of meteorites. Oldest known stars in our galaxy support this estimate. Solar system formed from a collapsing dust and gas cloud. Sun formed at the center, with planets emerging from remaining disk material. This age is crucial for understanding cosmic evolution.

The solar system formed around 4.6 billion years ago when a giant cloud of gas and dust collapsed under its own gravity. This collapse triggered the formation of the Sun and planets through a process known as accretion. The solar system is relatively young compared to the universe as a whole. The universe is estimated to be approximately 13.8 billion years old, meaning our solar system formed about 9.2 billion years after the Big Bang.
What is the outer vs inner solar system?
The solar system divides into inner and outer regions. Inner solar system contains four planets closest to Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars. Outer solar system comprises four planets furthest from Sun: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune. Inner planets are rocky and smaller. Outer planets are gaseous and larger. Distance from Sun determines classification.
Inner planets have smaller sizes compared to outer planets. Inner planets’ diameters range from 4,879 km to 12,742 km, while outer planets’ diameters span from 49,528 km to 142,984 km. Inner planets possess rocky, metallic compositions, resulting in higher densities ranging from 5.4 g/cm³ to 5.5 g/cm³. Outer planets have gaseous compositions of hydrogen and helium, leading to lower densities between 0.7 g/cm³ and 1.6 g/cm³.
Inner planets lack prominent ring systems, whereas outer planets possess prominent rings. Saturn exhibits the most notable ring system among the outer planets. Inner planets have few or no moons. Outer planets boast numerous moons, with Jupiter having 79 known moons and Saturn having 62 known moons.
Inner planets orbit the Sun more quickly, with Mercury moving at an average speed of 47.4 km/s. Outer planets orbit more slowly, exemplified by Jupiter’s average speed of 13.1 km/s. Inner planets rotate on their axes more slowly, with Earth completing a rotation in 24 hours. Outer planets rotate more rapidly, as seen in Jupiter’s rotation period of 9.9 hours.
How far is the edge of the solar system?
The Oort Cloud extends from 2,000 to 100,000 astronomical units (AU) away from the sun. Edge of the solar system starts around 2,000 AU from the sun. AU equals 93 million miles or 149.6 million kilometers. Voyager 1, at 12.5 billion miles, would take 70,000 years to reach the inner edge.
The inner edge of the Oort Cloud is estimated to be between 1,000 au and 5,000 au from the Sun. The exact location remains uncertain due to the difficulty in observing such distant objects. Neptune, the outermost planet, orbits at an average distance of 4,000,000,000 kilometers from the Sun. Voyager 1, the most distant human-made object, has traveled approximately 125 au from the Sun. The farthest detected object in our solar system is the dwarf planet Eris, located about 13,000,000,000 kilometers from the Sun.
What are fun facts about the solar system?
Fun facts about the solar system are listed below.
- The solar system consists of fascinating objects and extreme environments.
- One million Earths could fit inside the Sun, demonstrating its immense size.
- Earth could fit 1.3 million times into the Sun, further emphasizing the Sun’s vastness.
- The Sun accounts for 99% of the solar system’s mass, dominating the entire system.
- The Sun is over 90 million miles away from Earth, illustrating the vast distances in space.
- You can’t stand on Uranus due to its gaseous composition and low gravity.
- The whole of Mars is as cold as the South Pole, with average temperatures of -80°F (-60°C).
- Saturn’s rings are 90% water ice, mixed with 10% rock debris.
- Jupiter’s largest moon, Ganymede, has a salty ocean with more water than Earth.
- Mercury takes roughly three Earth months to orbit the Sun, completing its journey in 88 Earth days.
- Uranus spins sideways with its axis tilted at 98 degrees, causing extreme seasons.
- Jupiter’s moon Io is the most volcanically active body in the solar system.
- Venus is the hottest planet, not Mercury, with surface temperatures reaching 462°C (863°F).
- Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system, measuring 4,879 kilometers (3,031 miles) in diameter.
- The solar system formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago from a collapsing gas and dust cloud.
- The solar system includes planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and various smaller bodies.
- The solar system’s mass totals approximately 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms, with the Sun comprising the vast majority.

Sun comprises 99.8% of the solar system’s mass. Jupiter, largest planet, measures 11 times Earth’s diameter. Saturn’s rings are 93% water ice. Earth is 71% water, mostly salty oceans. Mars hosts Olympus Mons, tallest volcano, standing 27 km high. Jupiter’s Great Red Spot fits three Earths inside.
You can’t stand on Uranus due to its gaseous composition and low gravity. The whole of Mars is as cold as the South Pole, with average temperatures of -80°F (-60°C). Saturn’s rings are 90% water ice, mixed with 10% rock debris. Jupiter’s largest moon has a salty ocean with more water than Earth, containing more liquid than all of Earth’s oceans combined. Mercury takes roughly three Earth months to orbit the Sun, completing its journey in 88 Earth days.
Uranus spins sideways with its axis tilted at 98 degrees, causing extreme seasons. Jupiter’s moon Io is volcanic chaos, being the most volcanically active body in the solar system. Venus is the hottest planet, not Mercury, with surface temperatures reaching 462°C (863°F). Mercury is the smallest planet in the solar system, measuring 4,879 kilometers (3,031 miles) in diameter.
The solar system formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago from a collapsing gas and dust cloud. The solar system includes planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and various smaller bodies. The solar system’s mass totals approximately 1.989 x 10^30 kilograms, with the Sun comprising the vast majority.

