James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Definition, Comparison, Discoveries
The James Webb Space Telescope is the largest and most advanced space observatory ever built. It features a 6.5-meter primary mirror and operates in the infrared spectrum. JWST conducts infrared astronomy to investigate the origins of first stars and galaxies, planet formation, and exoplanet atmospheres. The telescope’s instrument suite includes four main instruments: Near-Infrared Camera, Near-Infrared Spectrograph, Mid-Infrared Instrument, and Fine Guidance Sensor.
JWST surpasses the Hubble telescope in several aspects. Its 6.5-meter mirror is significantly larger than Hubble’s 2.4-meter mirror. JWST observes infrared spectra (0.6-28.5 microns), while Hubble focuses on visible light, ultraviolet, and near-infrared (0.1-2.5 microns). The resolution and sensitivity of JWST exceed Hubble’s by 10-100 times. JWST orbits 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, while Hubble orbits at an altitude of 540 kilometers.
JWST has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries since its launch. It detected methane, carbon dioxide, and dimethyl sulfide in the atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18 b. The telescope observed six enormous galaxies from 500-700 million years after the Big Bang. JWST captured images of galaxies forming when the universe was only 400 to 500 million years old. It produced detailed images of the Southern Ring Nebula and detected Earendel, a star located 12.9 billion light-years away.
James Webb Space Telescope orbits the Sun 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. It occupies the second Lagrange point (L2), a gravitationally stable location. L2 provides a constant distance from Earth and Sun, reducing thermal noise.
The James Webb telescope cost $10 billion in total to build. Development and construction from 2003 to 2018 amounted to $8.7 billion. Launch and deployment from 2018 to 2021 required $0.8 billion. The first 5 years of operations from 2021 to 2026 cost $0.5 billion.
JWST launched on December 25, 2021, at 07:20 UTC. The launch occurred from Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. An Ariane 5 rocket carried out the launch, marking a significant space exploration milestone.
The telescope is named after James E. Webb, NASA’s second administrator from 1961 to 1968. Webb oversaw Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs, crucial for landing humans on the Moon. NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe announced the telescope’s naming in 2002, recognizing Webb’s leadership in balancing human spaceflight and science during NASA’s early years.
JWST collects light from distant objects using its 6.5-meter primary mirror. A secondary mirror intercepts and reflects light to scientific instruments. Instruments analyze infrared light, revealing celestial objects’ composition and motion. A large sunshield, about the size of a tennis court, blocks sunlight and heat. The telescope stays precisely aligned using a network of 132 actuators and sensors.
What is James Webb Space Telescope?
James Webb Space Telescope is a powerful space observatory launched in December 2021, representing the largest and most advanced telescope ever built. The telescope features a 6.5-meter primary mirror and operates in the infrared spectrum, allowing it to study cool or distant objects undetectable by other telescopes. JWST conducts infrared astronomy to answer fundamental questions about the universe, including the origins of first stars and galaxies, planet formation, and exoplanet atmosphere composition. Astronomers use the James Webb Space Telescope to investigate properties of black holes and dark matter, as well as study star and planetary system formation. NASA leads the James Webb Space Telescope project in partnership with the European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency, building on the legacy of previous space telescopes like Hubble.
James Webb Space Telescope instrument suite includes four main instruments. The Near-Infrared Camera captures high-resolution images in the near-infrared spectrum. The Near-Infrared Spectrograph studies atmospheric composition of distant planets and moons. The Mid-Infrared Instrument studies star and planetary system formation in our galaxy. The Fine Guidance Sensor provides precision navigation and control for the telescope.
James Webb Space Telescope discoveries revolutionize our understanding of the universe. James Webb Space Telescope captures stunning images with 10-100 times higher resolution than Hubble. James Webb Space Telescope has a 6.5-meter primary mirror made of 18 hexagonal segments. James Webb Space Telescope has a tennis court-sized sunshield maintaining -240°C temperature. James Webb Space Telescope orbits in a halo around Lagrange point 2. James Webb Space Telescope is expected to operate for at least 5 years, with a 10-year goal.
How does James Webb telescope compare to Hubble telescope?
James Webb Space Telescope complements Hubble telescope. Webb’s 6.5-meter mirror surpasses Hubble’s 2.4-meter mirror. Webb observes infrared spectra (0.6-28.5 microns), while Hubble focuses on visible light, ultraviolet, and near-infrared (0.1-2.5 microns). Webb peers deeper into space, detecting fainter objects. Webb’s resolution and sensitivity exceed Hubble’s by 10-100 times. Webb orbits 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
JWST captures deep field images in a fraction of the time required by Hubble. JWST produces comparable deep views in just over 12 hours, whereas Hubble needed weeks of exposure time for its deepest images. JWST’s infrared capabilities allow it to peer through dust and gas, observing objects obscured in visible light. JWST observes the universe as it existed just 200 million years after the Big Bang, while Hubble’s observations extend to about 13.4 billion years ago.
JWST orbits at the second Lagrange point (L2), approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. Hubble orbits Earth at an altitude of 340 miles (540 kilometers). JWST focuses primarily on studying the formation of the first stars and galaxies, evolution of planetary systems, and composition of distant planets’ atmospheres. Hubble has observed a wide range of astronomical objects and phenomena.
JWST images appear different from Hubble’s due to its infrared focus. JWST images reveal thermal signatures of objects, providing insights into their composition and temperature. JWST represents a significant technological advancement over Hubble. JWST incorporates advanced detector technology, a cryogenic cooling system, and a sophisticated sunshield. Engineers launched JWST on December 25, 2021, aboard an Ariane 5 rocket from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana.
What discoveries have been made by James Webb telescope?
The discoveries made by James Webb telescope are listed below.
- James Webb detected methane, carbon dioxide, and dimethyl sulfide in the atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18 b.
- James Webb Space Telescope observed six enormous galaxies from 500-700 million years after the Big Bang.
- JWST Captured images of galaxies forming when the universe was only 400 to 500 million years old.
- JWST produced detailed images of the Southern Ring Nebula.
- James Webb detected Earendel, a star located 12.9 billion light-years away.
- James Webb telescope observed protostars in the Tarantula Nebula.
- Webb telescope detected galaxies GN-z11 and UDFy-38135539 as they appeared just 400 million years after the Big Bang.
- JWST observed “universe breaker” galaxies with high star formation rates.
- JWST detected water vapor, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, sodium, and potassium in exoplanet atmospheres.
- James Webb telescope found evidence of a supermassive black hole in galaxy GN-z11.

The James Webb Space Telescope has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries since its launch in December 2021. JWST detected methane, carbon dioxide, and dimethyl sulfide in the atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18 b, located 111 light-years from Earth. The telescope observed six enormous galaxies from 500-700 million years after the Big Bang, challenging current models of galaxy formation. JWST captured images of galaxies forming when the universe was only 400 to 500 million years old, providing insights into early cosmic structure and evolution.
The telescope produced breathtaking images of the Southern Ring Nebula, showcasing its intricate structure and composition. JWST detected Earendel, a star located 12.9 billion light-years away, making it one of the most distant stars ever observed. The telescope observed protostars in the Tarantula Nebula, a star-forming region in the Large Magellanic Cloud, helping scientists understand early stages of star formation.
JWST detected two galaxies, GN-z11 and UDFy-38135539, as they appeared just 400 million years after the Big Bang. The telescope observed “universe breaker” galaxies forming stars at rates difficult to explain with current theories. JWST detected water vapor, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, sodium, and potassium in exoplanet atmospheres. The telescope found evidence of a supermassive black hole at the center of galaxy GN-z11, which appears as it was just 400 million years after the Big Bang.
Has James Webb space telescope found life?
James Webb Space Telescope has not found definitive evidence of alien life. JWST detected methane in an exoplanet’s atmosphere. Methane is a potential biosignature. Recent observations show intriguing features on distant planets. Scientists emphasize these findings are preliminary. Further confirmation is required. Detecting extraterrestrial life remains challenging.
JWST’s instruments play a crucial role in the search for life. The Near-Infrared Spectrograph and Mid-Infrared Instrument analyze light passing through exoplanet atmospheres. These instruments can detect subtle changes in atmospheric composition, including gases potentially produced by living organisms. JWST’s capabilities have enhanced our ability to search for extraterrestrial life through high-resolution spectroscopy.
Scientists analyze data collected by JWST to identify potential biosignatures. The telescope has detected complex organic molecules in the Orion Nebula, 1,300 light-years from Earth. JWST observations of the TRAPPIST-1 system, 39 light-years away, contribute to our understanding of potentially habitable worlds. The search for biosignatures continues as JWST observes and analyzes more exoplanet atmospheres.
How far away is James Webb from Earth?
James Webb Space Telescope orbits the Sun 1.5 million kilometers (930,000 miles) from Earth. Webb occupies the second Lagrange point (L2), a gravitationally stable location. L2 provides a constant distance from Earth and Sun, reducing thermal noise. Webb follows a halo orbit around L2, using thrusters and gravitational forces to maintain position.

Where is the James Webb telescope located?
The James Webb Space Telescope orbits the Sun 1.5 million kilometers (1 million miles) from Earth at the second Lagrange point (L2). L2 provides a stable environment for unobstructed observations. Webb follows a halo orbit around L2, completing one revolution every 6 months. This location enables precise observations of faint, distant celestial objects.
James Webb’s current position in the sky is within the Sagittarius constellation. The telescope’s right ascension is 19h 18m 36s. Its declination is -27° 45′ 58″. These coordinates pinpoint the James Webb telescope’s exact location in space.
How far can JWST see?
JWST observes objects 13.5 billion light-years away. JWST looks back in time 13.5 billion years. Objects at this distance existed 400 million years after the universe began. JWST sees these ancient objects as they appeared billions of years ago. Light from distant objects takes time to travel across space.
JWST observed the galaxy GN-z11, located 33.8 billion light-years away. GN-z11 existed 400 million years after the Big Bang and is one of the most ancient objects in the universe. JWST orbits 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth at the second Lagrange point (L2). JWST observes the universe in unprecedented detail from this location, using advanced instruments to measure light from distant objects.
How much did the James Webb telescope cost to build?
James Webb Space Telescope cost $10 billion in total. Development and construction from 2003 to 2018 amounted to $8.7 billion. Launch and deployment from 2018 to 2021 required $0.8 billion. First 5 years of operations from 2021 to 2026 cost $0.5 billion. NASA provided $8.7 billion as primary funding source.
Who funded the James Webb telescope?
NASA funded and led the James Webb Space Telescope development, costing $8.7 billion USD. NASA oversaw design, testing, launch, and operations. Canadian Space Agency and European Space Agency partnered as supporting agencies. CSA contributed instruments. ESA provided the Ariane 5 rocket for launch.
The European Space Agency (ESA) was a major funding contributor, providing $810 million for the James Webb Space Telescope. ESA’s total contribution reached $1.3 billion, accounting for 15% of the project’s funding. The agency supplied the Ariane 5 rocket for the telescope’s launch and funded the Near-Infrared Spectrograph instrument for €300 million.
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) played a crucial role in funding, contributing $340 million to the James Webb Space Telescope. CSA’s contribution represented 5% of the total funding. The agency developed the Fine Guidance Sensor and Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph, investing CAD 200 million in each instrument.
How much does James Webb telescope cost to maintain?
James Webb Space Telescope maintenance costs total $50 million annually. Operational expenses reach $187 million per year. Maintenance and repairs constitute a significant portion of the $1.1 billion budget allocated for 2022-2027. These costs ensure optimal performance for studying the universe in infrared light.
How big is James Webb telescope?
James Webb Space Telescope features a massive 6.5-meter (21.3-foot) primary mirror. Primary mirror area spans 25 square meters (269 square feet). Sunshield measures 22 meters (72 feet) long and 12 meters (39 feet) wide. Telescope weighs 6,500 kg (14,300 pounds). JWST orbits 1.5 million kilometers from Earth at Lagrange point 2.
What are 10 fun facts about James Webb space telescope?
The fun facts about James Webb Space Telescope are listed below.
- The James Webb Space Telescope is named after NASA’s second administrator, James E. Webb.
- JWST is the largest space telescope in history.
- James Webb telescope orbits 1 million miles from Earth at the Earth-Sun L2 point.
- JWST sensors can detect the heat of a bumblebee as far away as the Moon.
- JWST primary mirror has a diameter of 21 feet (6.4 meters).
- The James Webb Space Telescope weighs over 13,000 pounds, equivalent to an adult African elephant.
- It took NASA and international partners 25 years to create this telescope.
- The cost to develop and launch the James Webb telescope was $10 billion.
- JWST has a 273 square feet light collection area for observing distant celestial objects.
- The James Webb Space Telescope is designed to last 5-10 years in space, with a potential lifespan of up to 20 years.
The James Webb Space Telescope was named after NASA’s second administrator, James E. Webb. NASA designed it as the largest space telescope in history. The telescope orbits 1 million miles from Earth at the Earth-Sun L2 point. Scientists equipped it with sensors that detect heat of a bumblebee as far away as the Moon. Engineers built the telescope with a primary mirror diameter of 21 feet (6.4 meters). The James Webb Space Telescope weighs over 13,000 pounds, equal to an adult African elephant. NASA and international partners took 25 years to create this remarkable instrument. The telescope cost $10 billion to develop and launch. It has a 273 square feet light collection area for observing distant celestial objects. Mission planners designed the James Webb Space Telescope to last 5-10 years in space, with potential for up to 20 years of operation.
When did the James Webb telescope launch?
James Webb Space Telescope launched on December 25, 2021, at 07:20 UTC. Launch occurred from Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. Guiana Space Centre has coordinates 5.3°N latitude, 52.7°W longitude. Launch date coincided with Christmas Day. Ariane 5 rocket carried out the launch, marking a significant space exploration milestone.
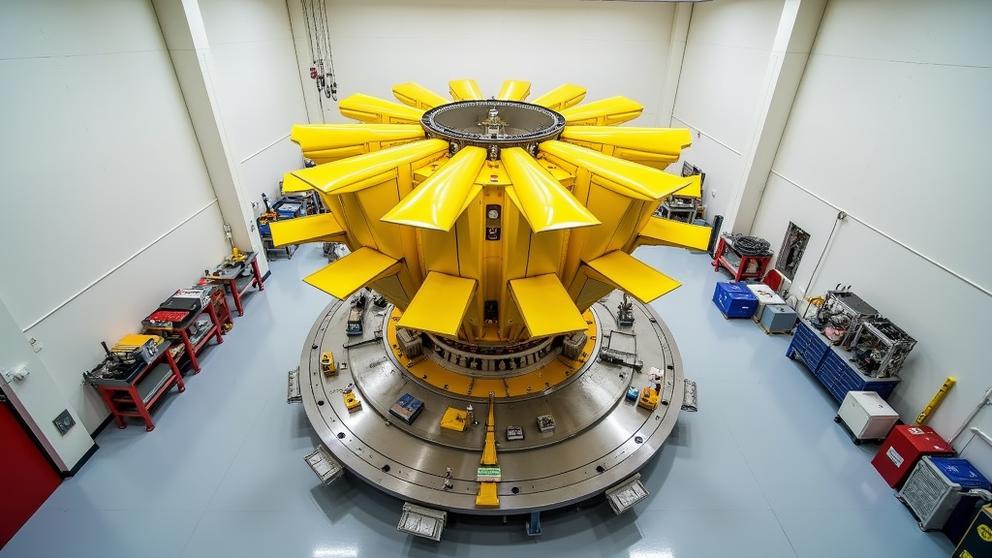
How long will the James Webb telescope last?
James Webb Space Telescope has an expected operational lifespan of 10 years. Webb telescope aims for 5 years of primary mission operations and 5 additional years of extended operations. Telescope’s complex design and orbit impact longevity. Webb’s 10-year lifespan allows extensive observations of early universe formation, planetary systems, and exoplanet atmospheres.
How did James Webb telescope get damaged?
James Webb Space Telescope suffered damage from a micrometeoroid hit in May 2022. Micrometeoroid struck one of the telescope’s 18 mirrors. NASA reported small but permanent damage occurred. Impact did not severely affect overall performance. Webb telescope remains fully operational. Telescope continues making groundbreaking observations of the universe despite damage.
The micrometeoroid collision created a small hole in the mirror segment, measuring approximately 0.25 millimeters in diameter. NASA engineers assessed the damage as irreversible, unable to be repaired or restored. The beryllium-gold segment struck has a thickness of only 4.3 millimeters, making it vulnerable to such impacts. The micrometeoroid traveled at an estimated speed of 10 kilometers per second when it hit the mirror.
The damage resulted in noticeable degradation of the telescope’s performance, in the mid-infrared wavelength range. NASA reported that the impact caused slight deformation of the mirror’s surface, affecting the telescope’s ability to focus light from distant objects. The incident highlighted the risks associated with operating a sensitive space-based observatory in the harsh environment of space, 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.
Who is the James Webb telescope named after?
James Webb Space Telescope is named after James E. Webb, NASA’s second administrator from 1961 to 1968. Webb oversaw Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs, crucial for landing humans on the Moon. NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe announced the telescope’s naming in 2002, recognizing Webb’s leadership in balancing human spaceflight and science during NASA’s early years.
NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe announced the decision to rename the telescope in 2002. The Next Generation Space Telescope was renamed as a tribute to Webb’s significant contributions to space exploration. James Webb Space Telescope is considered the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope.
Who made the James Webb telescope?
NASA, ESA, and CSA collaborated to create the James Webb Space Telescope. Northrop Grumman served as prime contractor. Ball Aerospace developed the optical system. Lockheed Martin created the spacecraft bus. The project involved scientists and engineers from over 20 countries. NASA led development, with ESA and CSA contributing to instruments and spacecraft. Final cost reached $8.7 billion in 2021.
The European Space Agency (ESA) made significant contributions to the James Webb Space Telescope. ESA developed the Near-Infrared Spectrograph instrument, which studies the formation of the first stars and galaxies in the early universe. ESA provided the Ariane 5 rocket used to launch the telescope on December 25, 2021, from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana.
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) played a crucial role in the telescope’s development. CSA contributed the Fine Guidance Sensor for navigation and the Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph instrument for scientific observations. The James Webb Space Telescope project involved numerous organizations and institutions, resulting in a powerful space observatory with a 6.5-meter primary mirror and a sunshield approximately 22 meters in diameter.
How was the James Webb telescope made?
The James Webb Space Telescope was made through a complex process spanning over two decades. Construction of the telescope began in 2004, led by Northrop Grumman as the primary contractor. Engineers designed the telescope to fold upon itself for launch, fitting inside the Ariane 5 rocket. The mirror of the telescope was built in segments, consisting of 18 hexagonal pieces each measuring approximately 1.5 meters in diameter. Ball Aerospace constructed the mirror segments using cryogenic testing techniques. The mirror was completed in 2016, marking a significant milestone in the telescope’s development.
Scientists developed innovative solutions to overcome numerous engineering problems during the telescope’s construction. The James Webb Space Telescope was made using advanced materials like beryllium to withstand the harsh conditions of space. Northrop Grumman led the development of the optical and mechanical systems, ensuring the telescope’s unique folding design would function properly. The four main instruments of the telescope were completed in 2017, relying on cryogenic cooling to operate effectively.
The structure of the James Webb Space Telescope folds to fit inside the launch vehicle, demonstrating its innovative design. Engineers faced and resolved various technical challenges throughout the development process. The Ariane 5 rocket successfully launched the telescope on December 25, 2021, marking the culmination of years of hard work and scientific advancement.
Where was the James Webb telescope built?
James Webb Space Telescope was built at Northrop Grumman’s Space Park facility in Redondo Beach, California. Construction spanned from 2003 to 2019 in a High Bay 1 cleanroom. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland made significant contributions. Over 1,500 people from Northrop Grumman, NASA, and partners were involved.
Northrop Grumman was responsible for designing and building critical elements of the telescope, including the spacecraft bus, sunshield, and optical system. The company integrated the 6.5-meter (21.3-foot) primary mirror, consisting of 18 hexagonal beryllium segments, into the spacecraft bus. Northrop Grumman collaborated with various partners and subcontractors throughout the construction process. Ball Aerospace in Colorado built the telescope’s mirrors, while institutions like the University of Arizona and UK Astronomy Technology Centre contributed instruments. The construction of the James Webb Space Telescope took over 20 years (2003-2021) and cost approximately $8.7 billion, with Northrop Grumman responsible for about 70% of the total cost.
Who owns the James Webb telescope?
The James Webb Space Telescope is jointly owned by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). NASA serves as the primary owner and operator of the telescope, having invested $8.7 billion in the project. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center manages the mission and oversees day-to-day operations. The European Space Agency is a major partner in the project, contributing €700 million and providing crucial components. ESA developed the Near-Infrared Spectrograph and Mid-Infrared Instrument for the telescope. ESA supplied the Ariane 5 rocket used for the telescope’s launch. The Canadian Space Agency acts as a junior partner, investing CAD 200 million in the mission. CSA developed the Fine Guidance Sensor and Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph for the telescope. Scientists from all three space agencies collaborate to operate the James Webb Space Telescope, conducting infrared astronomy to study the formation of early stars and galaxies, planetary system evolution, and distant planet atmospheres.
Who operates the James Webb telescope?
NASA operates the James Webb Space Telescope. NASA Goddard Space Flight Center led development and manages operations. Space Telescope Science Institute handles scientific operations. Northrop Grumman served as primary contractor. European Space Agency and Canadian Space Agency contributed instruments and components. JWST launched on December 25, 2021, after delays and cost overruns totaling $8.7 billion.
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, manages the day-to-day operations and scientific mission of the James Webb Space Telescope. STScI operates under contract with NASA and is run by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA). The institute coordinates observation scheduling, data analysis, and scientific research support for the telescope. STScI oversees the selection of observing proposals from astronomers worldwide.
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, handles overall mission operations for the James Webb Space Telescope. ESA provided the Ariane 5 launch vehicle and the Near-Infrared Spectrograph instrument. CSA contributed the Fine Guidance Sensor and the Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph instrument. The telescope has a primary mirror diameter of 6.5 meters and a total mass of approximately 6,500 kg. It operates at a temperature of around 40 Kelvin and observes the universe in the infrared spectrum, spanning wavelengths from 0.6 to 28.5 micrometers.
How does the James Webb telescope work?
James Webb Space Telescope collects light from distant objects using its 6.5-meter primary mirror. Secondary mirror intercepts and reflects light to scientific instruments. Webb’s large size enables observation of fainter objects. Instruments analyze infrared light, revealing celestial objects’ composition and motion. Webb orbits 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, maintaining stable temperatures for precise observations in space.
The James Webb telescope utilizes specialized capabilities to enhance its observations. It uses infrared light to study objects up to 13.5 billion light-years away. The telescope orbits the Earth-Sun Lagrange point, approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. A large sunshield, about the size of a tennis court, blocks sunlight and heat. This shielding keeps the telescope’s instruments extremely cold, at temperatures below -230°C. The telescope stays precisely aligned using a network of 132 actuators and sensors.
How does the JWST detect exoplanets?
JWST detects exoplanets using transit photometry method. Planets passing in front of stars cause mini-eclipses. JWST measures star light dimming to determine planet size. Transit method identifies exoplanets through periodic starlight dimming. JWST analyzes light passing through exoplanet atmospheres via transmission spectroscopy. Infrared observations characterize atmospheric temperature and composition of distant exoplanets.
Direct imaging serves as another crucial method for JWST to detect exoplanets. JWST uses a coronagraph to block the star’s light for direct imaging of exoplanets. Guyon et al. researched coronagraph techniques in 2006, paving the way for this advanced imaging capability.
JWST views infrared light to study exoplanet atmospheres with unprecedented detail. JWST uses spectrographs to detect chemical fingerprints in exoplanet atmospheres. Spectrographs identify methane, carbon dioxide, and water in exoplanet atmospheres. Tinetti et al. investigated spectroscopic detection of exoplanet atmospheres in 2013, laying the groundwork for JWST’s capabilities.
JWST detected signs of water vapor in the atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18b. Tsiaras et al. reported the detection of water vapor on K2-18b in 2019. JWST detected methane and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere of exoplanet WASP-96b. Nikolov et al. studied the atmosphere of WASP-96b in 2018, providing valuable insights for JWST’s observations.
JWST enables scientists to study exoplanet atmospheres in unprecedented detail. JWST provides insights into the formation and evolution of planetary systems. JWST has opened a new era in exoplanet research since its launch in December 2021.
What are the main parts on the James Webb telescope?
The main parts on the James Webb telescope are listed below.
- Optical Telescope Element (OTE): Core light-gathering component with a 6.5-meter primary mirror (18 gold-coated beryllium segments) and a 0.74-meter secondary mirror.
- Fine Steering Mirror: Precise adjustments for pointing and stabilization.
- Instrument Module: Houses four main science instruments for infrared light detection and analysis.
- Sunshield: Protects the telescope from the sun’s heat and light, measuring 22 meters in diameter and maintaining instrument temperature at approximately 40 K.
- Spacecraft Bus: Provides essential functions for telescope operation, including power generation, communication, and navigation systems.
The James Webb Space Telescope consists of seven main parts. The Optical Telescope Element (OTE) forms the core of the telescope’s light-gathering capability. The OTE includes a 6.5-meter diameter primary mirror made of 18 hexagonal beryllium segments coated in gold. A secondary mirror measuring 0.74 meters in diameter reflects light from the primary mirror to the instrument module. The Fine Steering Mirror makes precise adjustments for pointing and stabilization.
The Instrument Module houses four main science instruments for detecting and analyzing infrared light. The Sunshield protects the telescope from the sun’s heat and light, measuring 22 meters in diameter. The Sunshield maintains the instrument temperature at approximately 40 K. The Spacecraft Bus provides essential functions for telescope operation, including power generation, communication, and navigation systems.
What is the mission of James Webb space telescope?
James Webb Space Telescope, built by NASA, ESA, and CSA, studies the universe in infrared light. JWST seeks to understand first stars and galaxies in the early universe. JWST observes star and planetary system formation. JWST investigates exoplanet atmospheres and galaxy evolution over cosmic time. JWST orbits the Sun-Earth L2 point, revealing cosmic mysteries.
The James Webb Space Telescope investigates cosmic history and origins. It examines cosmic history from the Big Bang to the present day (Gardner et al., 2006). The telescope uncovers universe history by searching for the first stars and galaxies that formed around 13.5 billion years ago (Bunker et al., 2004). James Webb Space Telescope sheds light on the origins of planetary systems and reveals the birth of stars in various environments (Mather et al., 2014).
The James Webb Space Telescope studies celestial bodies and phenomena. It investigates exoplanets and their atmospheres to determine their potential for hosting life (Beichman et al., 2010). The telescope explores dust clouds that give birth to stars and planetary systems. James Webb Space Telescope examines the formation and evolution of galaxies, including the Milky Way.
The James Webb Space Telescope advances scientific understanding of the cosmos. It answers questions about the formation and evolution of galaxies, stars, and planetary systems (Clampin, 2011). The telescope’s infrared capabilities allow scientists to study objects too cool or distant to be detected otherwise (Clampin et al., 2010). James Webb Space Telescope enables space observation in unprecedented detail, providing deeper insights into the universe’s history and origins.
Why is the James Webb telescope important?
James Webb Space Telescope revolutionizes astronomy with unprecedented sensitivity and resolution. JWST observes distant galaxies, revealing universe evolution over billions of years. JWST studies planetary systems, searches for extraterrestrial life, and examines early star formation. JWST’s infrared capabilities detect cool, distant objects invisible to other telescopes. JWST’s sensitivity surpasses Hubble’s by 100 times, offering unparalleled cosmic insights.
James Webb telescope reveals new planets around distant stars. Researchers search exoplanet atmospheres for signs that could sustain life, characterizing their composition in detail. The telescope conducts infrared astronomy to uncover hidden cosmic phenomena. Astronomers hunt for unobserved formations in the early universe, exploring deep space objects billions of light-years away. The telescope’s primary mirror measures 6.5 meters in diameter, detecting wavelengths from 0.6 to 28.5 micrometers. It orbits at the L2 Lagrange point, 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, maintained at temperatures between -240°C and -270°C for optimal performance.
Where can you watch a James Webb telescope live stream?
NASA website hosts James Webb Space Telescope live streams at nasa.gov/live. NASA’s YouTube channel broadcasts live footage at youtube.com/nasa. Space Telescope Science Institute offers streams at youtube.com/stsci. Virtual Telescope Project provides additional coverage at virtualtelescope.eu. Facebook Live and Twitter feature live streams. Webcasts include expert commentary and mission activities.
Where can you download 4k wallpaper photos made by James Webb Space telescope?
NASA’s official website offers a full image collection of James Webb Space Telescope wallpapers with download options. Users have access to high-resolution 4K Ultra HD images through NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Flickr account. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Facebook page regularly posts stunning captures for download.
The r/Wallpapers community on Reddit features a dedicated thread for James Webb Space Telescope wallpapers in 4K Ultra HD. 4K Ultra HD Wallpaper Icon AI generates high-resolution wallpapers based on James Webb Space Telescope captures. Stock photo websites like Unsplash and Pexels provide free Creative Commons images of JWST captures.
Specialized websites offer phone wallpapers and backgrounds optimized from James Webb images. iPhone users will find James Webb iPhone wallpapers on websites like iPhone Wallpapers and WallpaperSafari. Websites such as Wallpaper Engine and Mobiles24 provide a wide range of JWST-inspired wallpapers for various devices.
Getty Images and Shutterstock offer James Webb Space Telescope stock images, including 4K Ultra HD wallpapers for purchase. The James Webb Space Telescope Captures website showcases a curated collection of stunning images taken by the telescope. Space enthusiasts will find an abundance of high-quality wallpapers by searching for “James Webb Space Telescope wallpaper” on popular search engines.
