Hubble Space Telescope: Definition, Launch Date, Discoveries, Costs, History
The Hubble Space Telescope is a renowned space-based observatory orbiting Earth at an altitude of 340 miles. Launched on April 24, 1990, aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery, Hubble has dramatically altered our view of the universe. The telescope features a 2.4-meter primary mirror and two solar arrays generating 2,800 watts of power. Hubble has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries, including pinpointing the age of the universe to approximately 13.8 billion years and discovering two moons of Pluto, Nix and Hydra, in 2005. The telescope cost approximately $2 billion to build between 1970 and 1990, with total costs exceeding $13 billion by 2019. Scientists proposed a space-based telescope in the 1970s, and NASA began developing the concept in 1977. Hubble uses a Cassegrain design with two curved mirrors to collect and focus light from celestial objects. The telescope’s 13.2m length allows for detailed observations of distant objects, capturing high-resolution images and spectra in visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared light.
What is a Hubble space telescope?
Hubble Space Telescope is a renowned space-based observatory orbiting Earth at an altitude of 340 miles. Hubble Space Telescope has dramatically altered our view of the universe since its launch in 1990. Hubble Space Telescope is a reflecting telescope of the Cassegrain type with a primary mirror diameter of 2.4 meters and a focal length of 57.6 meters. Hubble Space Telescope captures high-resolution images of celestial objects in multiple wavelengths, including ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center operates the spacecraft and its systems, while the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, is responsible for the scientific operation of the telescope.
The Hubble Space Telescope instruments include the Wide Field Camera 3, Cosmic Origins Spectrograph, Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph, and Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer. These instruments enable observations in visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared light spectra. The Hubble Space Telescope features a 2.4-meter primary mirror and two solar arrays generating 2,800 watts of power.
The Hubble Space Telescope description includes its weight of 11,110 kilograms and power consumption of 2,800 watts. The Hubble Space Telescope has determined the universe’s expansion rate, observed star and galaxy formation, and studied dark energy properties. NASA launched the Hubble Space Telescope on April 24, 1990, aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. The Hubble Space Telescope was named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and represents a collaboration between NASA and the European Space Agency.
How far can the Hubble telescope see?
The Hubble Space Telescope observes objects up to 13.4 billion light-years away from Earth. Hubble’s farthest detected galaxy, GN-z11, exists at this extreme distance. The telescope’s theoretical limit extends to 46 billion light-years due to the expanding universe model. Hubble’s general observational range covers several billion light-years, allowing study of various celestial objects. Ground-based telescopes before Hubble could only see 6-7 billion light-years into space. Hubble effectively doubled this range, enabling scientists to examine half of the universe’s cosmic history. The telescope orbits Earth at an altitude of 547 kilometers. Hubble’s position above the atmosphere provides clear, undistorted views across multiple wavelengths. The space-based observatory captures ultraviolet and near-infrared light impossible to detect from the ground. Hubble’s advanced instruments and stable orbit revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos since its 1990 launch.
What are 10 fun facts about the Hubble space telescope?
The fun facts about the Hubble Space Telescope are listed below.
- The Hubble Space Telescope was named after astronomer Edwin Hubble, who made groundbreaking discoveries about the universe’s expansion.
- Hubble Space Telescope has the size of a large school bus, measuring 43.5 feet in length and 14 feet in diameter.
- Hubble Space Telescope weighs 24,500 pounds, equivalent to the weight of two large elephants.
- Hubble Space Telescope uses two 25-foot solar panels for energy, generating 2,800 watts of power.
- Hubble Space Telescope orbits Earth at 17,000 miles per hour, completing one orbit every 97 minutes.
- Hubble Space Telescope takes 15 minutes to rotate 90 degrees, which is slow compared to other spacecraft.
- Hubble Space Telescope is extremely accurate in locking onto targets, achieving a pointing precision of 0.01 arcseconds.
- Hubble Space Telescope confirmed the existence of black holes in galaxy centers, revolutionizing our understanding of cosmic structures.
- Hubble Space Telescope discovered ancient galaxies from the early universe, providing insights into cosmic formation and evolution.
- Hubble Space Telescope was updated by five space shuttle missions over 25 years, ensuring its continued operation and technological advancement.
Hubble Space Telescope orbits Earth at 340 miles altitude. Hubble completes one orbit every 97 minutes. Hubble travels at 15,000 miles per hour. Hubble’s mirror measures 7.8 feet in diameter. Hubble has operated for over 30 years. Hubble determined the universe’s expansion rate. Hubble captured first black hole images. Hubble measures 43.5 feet long and 14.2 feet wide.
Hubble Space Telescope takes 15 minutes to rotate 90 degrees, which is slow compared to other spacecraft. Hubble Space Telescope is extremely accurate in locking onto targets, achieving a pointing precision of 0.01 arcseconds. Hubble Space Telescope confirmed the existence of black holes in galaxy centers, revolutionizing our understanding of cosmic structures. Hubble Space Telescope discovered ancient galaxies from the early universe, providing insights into cosmic formation and evolution. Hubble Space Telescope was updated by five space shuttle missions over 25 years, ensuring its continued operation and technological advancement.
What type of telescope is the Hubble space telescope?
Hubble Space Telescope is a reflecting telescope, specifically a Ritchey-Chrétien Cassegrain design. Cassegrain telescopes use curved primary and secondary mirrors to collect and focus light. Light travels through a curved path in the telescope. Primary mirror measures 2.4 meters in diameter. Secondary mirror measures 0.3 meters. Cassegrain design enables compact structure and high-resolution imaging.
Light enters the telescope and hits the primary mirror. The primary mirror bounces light to a smaller secondary mirror measuring 0.3 meters in diameter. The secondary mirror is convex shaped and positioned in front of the primary mirror. Light bounces off the secondary mirror and travels through a hole in the center of the primary mirror. The light then focuses onto a detector, such as a camera or spectrograph, at the focal plane.
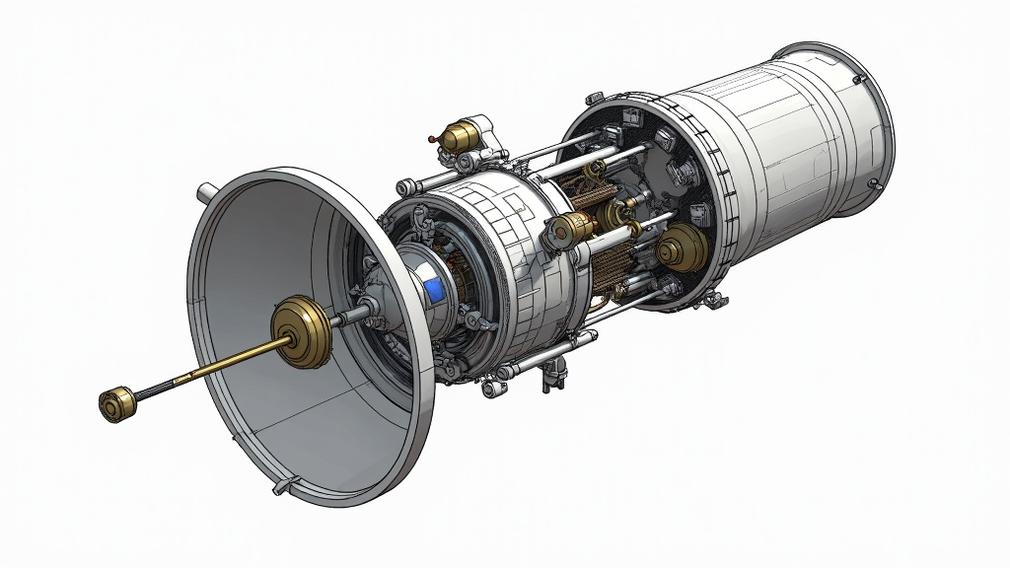
The Hubble Space Telescope uses a Ritchey-Chrétien telescope design. Ritchey-Chrétien is a type of Cassegrain reflector that uses a hyperbolic primary mirror and a convex secondary mirror. This design corrects for spherical aberration and coma, allowing Hubble to capture high-resolution images across the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared spectrum.
How is the Hubble telescope different compared to James Webb telescope?
James Webb Space Telescope has a 6.5-meter primary mirror, 2.7 times larger than Hubble’s 2.4-meter mirror. JWST observes in infrared wavelengths, peering through dust to see cooler objects invisible to Hubble. Hubble captures visible light and ultraviolet. JWST orbits 1.5 million kilometers from Earth, while Hubble orbits at 340,000 kilometers.
Hubble observes the universe in visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared wavelengths. James Webb focuses primarily on infrared wavelengths, including mid- and far-infrared. Webb’s infrared capabilities enable it to study cooler celestial objects and detect distant galaxies, stars, and planets.

James Webb offers higher sensitivity than Hubble, especially in the infrared range. Webb’s sensitivity exceeds Hubble’s by 10-100 times for infrared observations. Webb provides higher angular resolution, resolving objects about 2-3 times smaller than Hubble at certain wavelengths.
James Webb observes the universe in its earliest stages, studying objects that existed 400 million years after the Big Bang. Hubble focuses on objects from the more recent past, primarily within the last few billion years. Webb observes objects up to 13.6 billion light-years away, while Hubble’s limit is approximately 13.4 billion light-years.
When was the Hubble telescope launched?
Hubble Space Telescope launched on April 24, 1990, at 8:33:51 AM EDT from Kennedy Space Center. Space Shuttle Discovery deployed Hubble during STS-31 mission. Launch occurred from Pad 39B. Mission lasted 5 days, 1 hour, 16 minutes. Five-member crew included Commander Loren J. Shriver and Pilot Charles F. Bolden.

When was the Hubble telescope made?
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched on April 24, 1990. NASA built the large space telescope in the 1980s. The first components were designed in the 1940s. The Hubble Space Telescope has been operational since its 1990 launch. The Space Shuttle Discovery carried it into orbit.
Funding for the Hubble Space Telescope project began flowing in 1977. Congress authorized the construction of the telescope in the same year. NASA and contractors, primarily Lockheed Corporation, built the Hubble Space Telescope throughout the 1980s. The European Space Agency contributed to the construction process. The telescope’s construction was completed in 1985.
The Space Shuttle Discovery launched the Hubble Space Telescope on April 24, 1990. The telescope was deployed into orbit around Earth at an altitude of approximately 340 miles. Hubble has been operational since its deployment, revolutionizing our understanding of the universe through numerous groundbreaking observations and discoveries.
When will the Hubble telescope retire?
Hubble Space Telescope is predicted to retire in the mid-2030s, with estimates suggesting 2037. NASA Administrator Michael D. Griffin stated the mission has been completed. Hubble has exceeded its 15-year design life, operating for over 32 years. NASA aims to keep the telescope operational until the mid-2030s, extending the mission in 2020 for five additional years.
How far is the Hubble space telescope from Earth?
Hubble Space Telescope orbits Earth at approximately 340 miles (547 kilometers) altitude. Precise distance varies due to orbital mechanics. Hubble’s orbit remains above Earth’s atmosphere at 320-340 miles (515-547 km). Altitude allows clear observations of distant celestial objects without atmospheric distortion. Periodic orbital adjustments maintain optimal positioning for observations.
Various sources have reported different altitudes for Hubble’s orbit over the years. The telescope had an initial altitude of 320 miles (515 km) when first launched. Some sources cite a specific orbit of 547 kilometres (340 miles). Other reports place Hubble at approximately 535 kilometers (332 miles) or 570 km above Earth.
Hubble’s altitude experiences changes over time due to several factors. The telescope’s orbit slowly degrades due to atmospheric drag, even at its high altitude. Periodic adjustments are made to maintain Hubble’s optimal height for observations. Space shuttle servicing missions have played a crucial role in repositioning the telescope and extending its operational lifetime.
How often does the Hubble orbit Earth?
Hubble orbits Earth every 96 minutes, completing 15 orbits per day. Hubble travels at 27,000 kph or 17,000 miles per hour around Earth. One orbit takes 96 minutes. Hubble experiences 15 sunrises daily due to its orbit. Hubble maintains a stable orbit at 340 miles altitude.
Hubble orbits Earth 27.3217 times during one lunar month. The lunar month lasts 27.3217 days, and Hubble’s orbital period is not synchronized with it. Hubble has completed approximately 175,200 orbits in its 30+ years of operation since its launch on April 24, 1990. Hubble’s orbit is slowly decaying due to atmospheric drag, with NASA estimating potential re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere in the 2030s.
What discoveries were made by the Hubble telescope?
The discoveries made by the Hubble telescope are listed below.
- Hubble pinpointed the age of the universe to approximately 13.8 billion years through observations of ancient stars and galaxies.
- Hubble telescope discovered two moons of Pluto, Nix and Hydra, in 2005.
- Hubble helped determine the rate of universe expansion, known as Hubble’s constant, to be approximately 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec.
- Hubble space telescope discovered supermassive black holes at the center of major galaxies, including our own Milky Way.
- Hubble traced galaxy evolution and formation over billions of years, providing insights into the early universe.
- Hubble observed dark matter through its gravitational effects on visible matter, supporting theories about the universe’s structure.
- Hubble discovered protoplanetary disks around young stars, revealing the birth of new planetary systems.
- Hubble telescope observed gamma-ray bursts, the most powerful explosions in the universe, helping scientists understand these cosmic phenomena.
- Hubble discovered Pluto’s moons Styx and Kerberos in 2011 and 2012.
- Hubble tracked Venusian cloud patterns and Martian dust storms, providing valuable data on planetary atmospheres.
- Hubble telescope monitored atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn, revealing their composition and dynamic weather systems.
- Hubble observed the accelerating expansion of the universe driven by dark energy, a discovery that earned the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Hubble telescope discovered the predicted appearance of a supernova in a distant galaxy cluster in 2019, confirming theoretical models of gravitational lensing.
Hubble discovered Dark Matter evidence through galaxy observations. Protoplanetary disks were detected around new stars. Gamma-Ray Bursts were studied extensively. Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9’s Jupiter collision was observed in 1994. M. Jee et al. used Hubble to map Dark Matter in Abell 2744. Hydra galaxy cluster was examined. Universe’s age was determined to be 13.8 billion years.
Hubble discovered supermassive black holes at the center of major galaxies, including our own Milky Way. Hubble traced galaxy evolution and formation over billions of years, providing insights into the early universe. Hubble observed dark matter through its gravitational effects on visible matter, supporting theories about the universe’s structure. Hubble discovered protoplanetary disks around young stars, revealing the birth of new planetary systems.
Hubble observed gamma-ray bursts, the most powerful explosions in the universe, helping scientists understand these cosmic phenomena. Hubble discovered Pluto’s moons Styx and Kerberos in 2011 and 2012, further expanding our knowledge of the Pluto system. Hubble tracked Venusian cloud patterns and Martian dust storms, providing valuable data on planetary atmospheres. Hubble monitored atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn, revealing their composition and dynamic weather systems.
Hubble observed the accelerating expansion of the universe driven by dark energy, a discovery that earned the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics. Hubble discovered the predicted appearance of a supernova in a distant galaxy cluster in 2019, confirming theoretical models of gravitational lensing.
What major breakthrough was made because of the Hubble?
Hubble Space Telescope determined the universe’s age to be 13.8 billion years with 100 million years uncertainty. Hubble discovered Pluto’s moons Nix and Hydra. Hubble measured the universe’s expansion rate at 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec. Hubble confirmed the Big Bang theory and provided evidence of dark energy through distant supernovae observations.
Hubble determined the rate of universe expansion, with researchers measuring Hubble’s constant to be approximately 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec in 1999. Astronomers pinned down the age of the universe to 13.8 billion years using Hubble data in 2003. Hubble observed comet impacts on Jupiter when Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 collided with the planet in 1994.
Hubble enhanced solar system exploration by discovering moons of Pluto named Nix and Hydra in 2005.
How much did the Hubble telescope cost to build?
Hubble Space Telescope cost approximately $2 billion to build between 1970 and 1990. Total costs exceeded $13 billion by 2019, including $11.3 billion for operations, maintenance, and upgrades since launch. James Webb Space Telescope, Hubble’s successor, has an estimated cost of $8.7 billion for its 2023 launch.
Hubble’s price tag grew substantially over time. Cumulative costs in 2015 dollars were estimated at $11.3 billion. The total cost since 1977, adjusted for inflation to 2021 dollars, amounted to $16 billion. This figure includes designing, building, launching, operating, and servicing Hubble over its 30-year lifespan.
How much does the Hubble telescope cost to maintain?
The Hubble Space Telescope requires approximately $100 million annually for maintenance. NASA allocates $93.3 million for the Hubble program in its fiscal year 2024 budget request. Maintenance costs cover personnel, operations, and equipment upkeep to ensure the telescope’s continued functionality.
Hubble has undergone several servicing missions throughout its operational life. Servicing Mission 3A (SM3A) in 1999 cost $136 million. Future repair missions for Hubble are estimated to cost between $1-2 billion, reflecting the telescope’s importance to space research.
The total cost of the Hubble Space Telescope program since 1977 is estimated at $16 billion, adjusted for inflation to 2021 dollars. This figure includes initial development, launch, and all servicing missions. Hubble’s price is difficult to quantify due to its numerous scientific discoveries and invaluable contributions to the scientific community.
What is the history of the Hubble telescope?
Scientists proposed a space-based telescope in the 1970s. NASA began developing the concept in 1977. Edwin Hubble’s discovery of universe expansion inspired the telescope’s name. Hubble Space Telescope launched in 1990. European Space Agency collaborated with NASA. Hubble exceeded its 15-year lifespan, making groundbreaking discoveries and capturing stunning cosmic images.
Funding for the Hubble Space Telescope began in 1977 with an initial allocation of $36 million from Congress. The telescope was designed and built throughout the 1970s and 1980s by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center and Lockheed Missiles & Space Company. NASA renamed the project from the Large Space Telescope to the Hubble Space Telescope in 1983, honoring astronomer Edwin Hubble who made groundbreaking discoveries about the expansion of the universe.

NASA launched the Hubble Space Telescope on April 24, 1990, aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. The shuttle lifted off from Kennedy Space Center’s Pad 39B at 8:33 AM EDT, carrying the telescope nestled in its payload bay. Astronauts placed Hubble into a low Earth orbit 340 miles above Earth’s surface, beginning its mission as the first major optical telescope in space.
Hubble has carried out over 1.2 million observations since its deployment. The telescope has been maintained and upgraded through five space shuttle servicing missions between 1993 and 2009. Engineers repaired a flaw in Hubble’s primary mirror during the first servicing mission in 1993, installing a corrective optics package called COSTAR. Subsequent missions replaced or upgraded Hubble’s solar panels, gyroscopes, and cameras, extending its lifespan beyond the initial 15-year expectation.
How old is the Hubble space telescope?
Hubble Space Telescope was first launched on April 24, 1990. NASA initially built Hubble to operate for 15 years. Hubble has exceeded its expected lifespan by decades. Hubble has been operational for 33 years as of October 2023. Astronomer Lyman Spitzer conceived Hubble in 1946.
Hubble Space Telescope has far exceeded its expected 15-year lifespan. Five space shuttle missions have serviced the Hubble Space Telescope, with the final mission occurring in 2009. Hubble Space Telescope continues to operate today, making new discoveries and pushing the boundaries of human knowledge about the universe.
Hubble Space Telescope has observed stellar groupings estimated to be 2 million years old. Astronomers have used the Hubble Space Telescope to capture stunning images of galaxies, stars, and planets. Hubble Space Telescope has determined the rate of expansion of the universe and observed the formation of stars and planets.
What flaw did the Hubble telescope have?
Hubble Space Telescope had spherical aberration in its primary mirror. Mirror’s outer edge was over-polished, creating excessive curvature. Curvature difference was 0.004 meters. Flaw caused light to focus at different points instead of a single focal point. Blurry images resulted from incorrect focusing. 1993 servicing mission installed COSTAR to correct aberration using small mirrors.
The root cause of the flaw was a measuring device malfunction during manufacturing. Crotty (1993) attributed the problem to this malfunction, which resulted in a lens askew in the reflective null corrector. The lens askew caused an optical system failure, significantly impacting the telescope’s ability to produce clear images. Ford (1993) explained how the incorrect mirror shape caused lens askew and image quality degradation.
The spherical aberration resulted in a larger point spread function, as explained by Krist (1993). The point spread function was 10 times larger than expected, with a full-width at half-maximum of approximately 1.5 arcseconds. Trauger (1994) noted that the mirror did not focus light to a single point, severely limiting the telescope’s ability to produce high-resolution images.
What did scientists do about the Hubble telescope flaw?
Scientists designed a corrective optics package for the Hubble telescope’s flawed mirror. Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) was installed during the 1993 servicing mission. WFPC2 used specialized lenses and mirrors to correct spherical aberration. Hubble’s image quality improved significantly. WFPC2 enabled sharp, clear images of distant space objects, leading to numerous astronomical discoveries.
The Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) was developed as an additional solution. COSTAR included corrective lenses placed in front of the telescope’s instruments to correct the spherical aberration. The combination of WFPC2’s internal optics and COSTAR successfully compensated for the 2 μm error in the primary mirror’s focal length.
Astronauts conducted a total of five servicing missions between 1993 and 2009 to repair and upgrade the Hubble telescope. During the second servicing mission in 1997, astronauts moved mirror segments to fine-tune the telescope’s optics. Engineers aligned the mirror segments to ensure proper configuration of the optical system. The servicing missions involved complex repairs and adaptations to the telescope’s design and operation in the space environment.
Who was the Hubble telescope named after?
The Hubble Space Telescope was named after Edwin Hubble, an American astronomer. Edwin Hubble made groundbreaking discoveries about the expansion of the universe and galaxy classification. NASA launched the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990 to honor Hubble’s pioneering work. The telescope has since revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos through numerous observations and discoveries.
Who invented the Hubble telescope?
NASA and ESA scientists and engineers invented the Hubble Space Telescope, not Edwin Hubble. Dr. C. Robert O’Dell led the NASA team as project scientist from 1972 to 1982. The telescope was named after Edwin Hubble, who discovered the expanding universe in 1929. Space Shuttle Discovery launched Hubble on April 24, 1990.
Multiple scientists and engineers contributed to the development of the Hubble Space Telescope. Dr. Lyman Spitzer first proposed the idea for a large space-based telescope in the 1940s. Dr. C. Robert O’Dell chaired a committee in 1962 that proposed a space telescope capable of observing the universe in visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared light. Dr. James Crocker served as the project manager during the telescope’s development.
The telescope was named after Edwin Hubble, a renowned American astronomer. Edwin Hubble discovered the expansion of the universe in 1929, fundamentally changing our understanding of the cosmos. NASA chose to name the telescope in his honor to recognize his significant contributions to astronomy. Edwin Hubble had no direct involvement in designing or constructing the space telescope that bears his name.
What was the mission of Hubble space telescope?
Hubble Space Telescope’s mission aimed to understand the universe’s formation and evolution. Hubble was designed to capture high-resolution images and spectra of distant objects. Launched in 1990, Hubble provides access to ultraviolet, visible, and infrared wavelengths. Hubble probes the cosmos in unprecedented detail, enabling groundbreaking discoveries about the universe’s history and expansion.
Hubble’s primary objective was to revolutionize our understanding of the universe’s history and expansion. The telescope measured the expansion rate of the universe at 67.8 ± 0.9 km/s/Mpc, contributing significantly to cosmological research. Hubble provided a clear vista of space by looking past Earth’s atmosphere, allowing scientists to study objects and events invisible from the ground.
The mission included studying celestial bodies within our solar system. Hubble investigated the composition, size, and orbits of asteroids. The telescope examined the atmospheres, surfaces, and rings of planets in unprecedented detail. Beyond our solar system, Hubble detected and characterized exoplanets, expanding our knowledge of planetary systems.
How does the Hubble telescope work?
Hubble telescope uses Cassegrain design with two curved mirrors. Primary mirror (2.4m diameter) collects light from celestial objects. Light reflects to smaller secondary mirror at tube’s front. Secondary mirror reflects light back through primary mirror’s hole. Light hits detector. Telescope’s 13.2m length focuses light from distant objects for detailed observations.
Light is focused onto digital cameras and spectrographs within Hubble’s instruments. The Wide Field Camera 3 captures images in visible, ultraviolet, and near-infrared light. The Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph analyzes light from celestial objects. The Cosmic Origins Spectrograph breaks light into component colors. These instruments capture high-resolution images and spectra, collecting data on light emission and absorption from distant objects.
Digital cameras convert the gathered light into electronic signals. The onboard computer processes and stores the captured images and data. Hubble transmits this information back to Earth via radio waves. NASA’s Deep Space Network receives these radio signals, allowing astronomers to study and understand the universe in unprecedented detail.
How big is the Hubble telescope?
Hubble Space Telescope measures 43.5 feet (13.2 meters) in length and 14 feet (4.2 meters) in width. Large spacecraft weighs 24,500 pounds (11,110 kilograms). Lockheed Martin manufactured Hubble with precise dimensions for space observation. NASA launched Hubble on April 24, 1990, aboard Space Shuttle Discovery. Hubble orbits Earth at 340 miles altitude.
How heavy is the Hubble telescope?
Hubble Space Telescope weighs 24,500 pounds (11,110 kilograms) at launch. Weight decreased to 24,000 pounds (10,886 kilograms) after Servicing Mission 4. Weight change resulted from replacing older, heavier components with newer, lighter ones. Weight impacts propellant requirements for orbit adjustments and spacecraft’s structural integrity.
Is the Hubble telescope still working in 2024?
Hubble Space Telescope operates in 2024. NASA announced Hubble’s restoration to science operations in April 2023. Hubble conducts scientific observations, collects data, and transmits it to Earth. Dr. Michael D. Griffin, NASA Administrator, confirmed Hubble’s good health. NASA expects Hubble to operate until at least 2030, potentially extending its mission to 2040.
Hubble telescope status shows it remains operational with some limitations. The telescope experienced a computer glitch in 2021, entering safe mode. Hubble was successfully recovered after a few weeks. The telescope is currently operating with three of its six gyroscopes. Hubble telescope age is approximately 33.5 years as of 2024. Hubble is one of the longest-operating space telescopes in history.
Hubble telescope operation continues at a reduced rate compared to its peak performance. The telescope is operating in a “reduced-gyro” mode. James Webb Space Telescope is the designated successor to Hubble. Webb was launched on December 25, 2021, to study the universe in the infrared part of the spectrum. NASA has no current plans to retire Hubble. Hubble telescope operation is expected to continue until at least 2030. The telescope’s orbit is expected to decay around 2030. NASA is exploring options to extend Hubble’s operation beyond 2030.
Where is the Hubble telescope located?
Hubble Space Telescope orbits Earth at 547 kilometers (340 miles) altitude. Space Shuttles drove Hubble to its orbit in 1990. Hubble orbits Earth every 97 minutes at 27,000 kilometers per hour. Hubble’s location allows servicing by shuttles and provides stable thermal conditions for instruments. Hubble’s orbit enables high-resolution observations without atmospheric distortion.
