Telescopes in Space
NASA and the European Union both have telescopes currently in space and has plans for more
You will be surpised to find out how many telescopes have been launched into space. We all know about the Hubble but there are quite a few more.
Having a telescope in space is a boon to astronomy. Not having to look through the Earth’s atmosphere means the telescope can see things that are simply impossible to see otherwise. Let’s first take a look at the obstacles of Earth based telescopes then we will look at the telescopes we currently have in space including one scheduled to launch in 2021.
The Obstacles to Earth Based Telescopes
The biggest obstacle any telescope faces is the Earth’s atmosphere. Think of the atmosphere around the Earth as a kind of thin soup. Even on perfectly clear and cloudness nights telescopes have to look through miles of swirling air. And this causes problems because telescopes magnify things which means that they also magnify turbulence and disturbances in the atmosphere.
Astronomers combat the problem of our atmosphere in a couple of different ways.
First off they put big telescopes on or near the top of mountains. This really pays off because you are now looking through miles less of atmosphere. It makes a big difference.
Secondly, with the biggest telescopes in the world the mirrors now have something called Adaptive Optics or “AO”. This is a brilliant electronic system that very slightly distorts mirrors anywhere on their surface to counter act disturbances in the atmosphere. It is a very fast process and this adaptive optics system detects fluctuations in the atmosphere and adjusts the mirror up to 2000 times every second!
We can avoid this problem if we put the telescope in space -outside the Earth’s atmosphere. And this is exactly what NASA and the European Space Agency has done, and continues to do. This gives us unparalled looks at the universe.
And it is why the Hubble Space telescope can get images like this Spiral Galaxy. (NGC 3147- photo credit NASA and STScI) This is a real picture.

So, what telescopes are in space and what telescopes are planned to go into space?
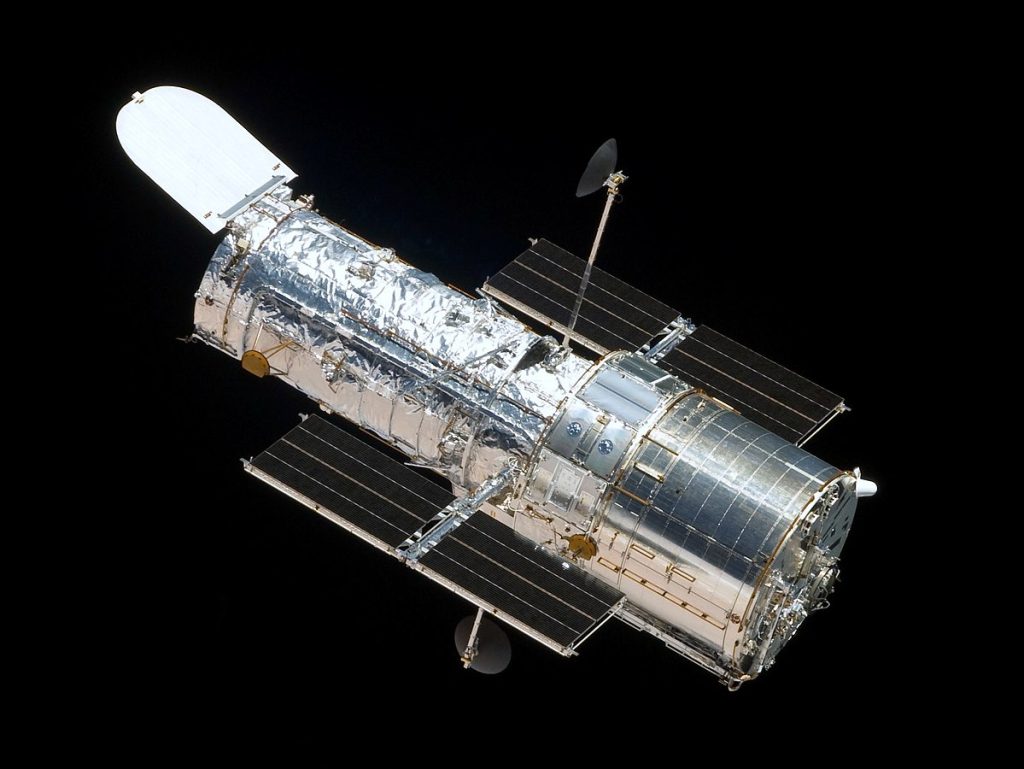
The Hubble Space Telescope
It is undoubtedly the most famous telescope that has ever been made. It has been in active use for almost 30 years now and it has captured images and made scientific discoveries that have changed the way we look at and understand the universe.
The main mirror in the Hubble is 2.4 meters in diameter (7.9 feet) . This mirror is what collects and magnifies light from objects in the universe. It is what makes the telescope possible. And th bigger the mirror the better! In the diagram below it is labeled as the primary mirror.

Credit: Ruffnax (Crew of STS-125) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons.
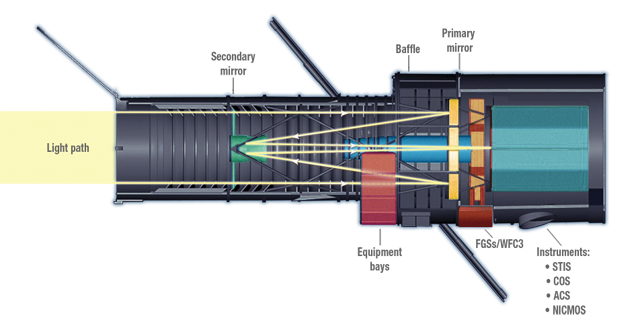
Image credit NASA and STScI
It is in a low orbit around the Earth and it has been in operation since 1990. It has literally changed our perception of the universe in so many different ways. And the pictures it has taken are simply astounding. You can see the pictures on the official Hubble website.
The James Webb Space Telescope
This is a space telescope that NASA is currently designing and building. It is scheduled to be launched in 2021.
It will ten times more powerful than the Hubble Telescope!
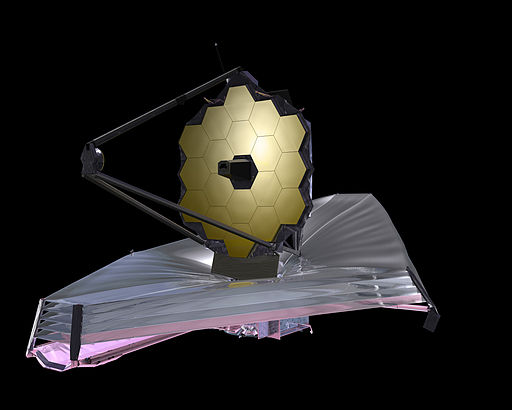
While this telescope will also be in space just like the Hubble telescope there are some significant differences with this one. .
First off this telescope will not be in Earth Orbit. It will circle around the Sun in an orbit similar to that of the Earth, and in a place where we can always communicate with it.
Secondly, and this is the big deal;. It is the next version of the Hubble. It is the super powered upgrade – the next generation of space telescope. The mirror of the James Webb is significantly larger than the Hubble. This one is 6.5 meters across (21 feet) whereas the Hubble mirror is 7.9 feet in diameter.
And because it is in space, and so much larger than the Hubble telescope, it is going to give us views of the universe like we have never before seen. I believe this telescope is going to discover things that radically change our view of the universe and in parrticular the beginning of the universe.
One of the goals of this telescope is to peer as deep into the beginnings of the universe as possible.
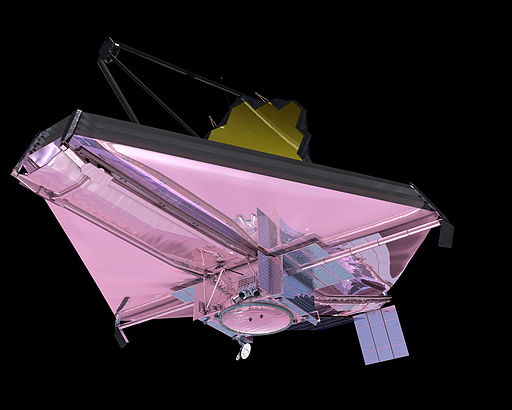
Notice in the first picture how between the space craft and the telescope you see a series of five layers of something. it looks like five layers of plastic or cloth. That is a heat shield. It will protect the telescope from the heat coming off the sun, the earth and the moon. This is necessary to keep the telescope operating at maximum efficiency.
The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST)

This is a specialized infra-red telescope that was launched in 2003 and is planned to be retired in 2020. It is in orbit around the Sun rather than around the Earth but in the same orbit, trailing behind the Earth.
The primary telescope mirror in it is 33 inches in diameter.
The Spitzer telescope and program is an amazing thing. You can learn more about it on the official website.
Kepler Space Telescope

2009- 2018 – now retired
It’s mission was to discover Earth sized planets around other stars that were in or near the habitable zone of these stars. It used a photometer to measure the brightness of stars over time. It’s an interesting technique where if a planet passes in front of a star that stars brightness would decrease. Kepler monitored over half a million stars in our galaxy and detected over 2,000 planets!
This technique is looking for something called a transit. Think of it as being the same exact thing as when the moon passes in front of our sun and we get an eclipse. The effect isn’t as dramatic with far away stars and planets but it is there!
The TESS Space Telescope (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite)

Launched in 2018 and still in service
This is the next generation of the Kepler Space Station and it has the same mission of looking for planets transiting in front of their stars . It is however much more capable and sensitive. And it is estimated that it will discover approximately 20,000 planets circling other stars.
Herschel Space Observatory

(2009-2013) Built and Launched by the European Space Agency
It was the largest infra-red telescope ever launched into space with a 3.5 meter mirror.
It had four different major missions including the investigation of star and galaxy formation. And the investigation of the molecular chemistry of the universe.
Hipparcos

Photo Credit: Michael Perryman [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
This telescope was launched by the European Space Agency in 1989 and it operated until 1994. It is now retired. It had an 11.4 inch Schmidt telescope on board and it’s mission was to accurately measure the positions of stars and other celestial objects.
IRAS -(Infra-red Astronomical Telescope)
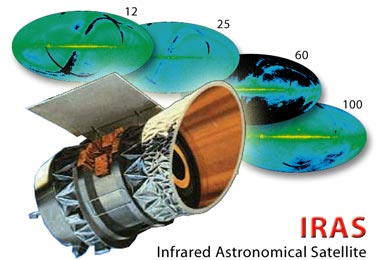
It was an infra-red telescope that was launched in 1983 and lasted about 11 months. It mapped about 96 percent of the sky in infra-red.
Other Telescopes that are/were in space
There have been dozens more telescopes launched into space. They all had very specialized missions including particle detection, observations in Gamma Rays, Ultra violet, X-rays, and microwave ranges.
Infra-Red Space Observatory (ISO)
It was launched by the European Space Agency in 1995 and operated until 1998. The Primary mirror was a Ritchey-Chretien type telescope with a diameter of 60cm. It was in an elliptical Earth orbit.
Akari
An infrared telescope built and launched by the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency. It operated from 2006 to 2011 and it had a 68.5 centimeter mirror. It was tasked to survey the entire sky in infra red.
